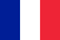
Nail fungus (lat. Onychomycosis) - in other words - a fungal infection of the nails. The disease can affect both fingernails and toenails. The reason is mainly the so-called dermatophytes, less frequently the fungi of the Candida species (yeasts) or molds.
Color changes, thickening and brittle nails are symptoms of fungus, but also of other skin and nail diseases, therefore, if such changes are found, it is necessary to contact a dermatologist and do bacteriological tests to detect the presence of fungi, too. as sowing.
It is estimated that about 50% of people whose nail plates on the palms and feet are rough and discolored suffer from nail fungus.
Causes and symptoms of nail fungus.
Nail fungus usually appears after a toenail fungus infection. According to studies, up to 42% of people suffer from toenail fungus and 21% of people suffer from nail fungus. Most often it is suffered by men (with the exception of candidiasis), rarely by children, but very often by older people. This disease affects all races equally.
More often in temperate climates, fungal nail infections are caused by dermatophytes, i. e. Trichophyton rubrum (70% of nail fungus cases), Trichophyton mentagrophytes (20% of all nail fungus cases ), Trichophyton interdigitale, Epidermophyton floccosum, Trichophyton tonshophyton violaceum, Microsporum gypseum soudanense and Trichophyton verrucosum. In the world, there are more and more cases of infection by fungi of other varieties, with the exception of dermatophytes and yeasts, namely Fusarium spp. , Scopulariopsis brevicaulis, Aspergillus spp. In some countries, Aspergillus spp. it is the cause of up to 15% of fungal cases.
You can become infected with a fungus, for example:
- in the pool,
- in sauna,
- putting on someone else's shoes or putting on someone else's socks,
- using someone else's manicure devices.
- The fungus often appears between the toes.
What is nail fungus?
Fungi that have already appeared on the skin of the feet can penetrate the skin and nail if the nail is damaged. It could be an injury or a nail cut too short. Nail diseases tend to affect weakened nails and, in particular, the use of nail polish and false nails contributes to the weakening.
In addition, some patients are predisposed to this type of infection due to various diseases that they suffer from. One of them are immunosuppressive disorders (immunosuppressive states) associated, for example, with HIV infection or chronic treatment with immunosuppressive drugs after organ transplantation, or with certain autoimmune diseases.
Another group of problems associated with an increased risk of nail fungus are hormonal disorders (Cushing's disease or syndrome, hypothyroidism, and others). This disease is more common in the presence of metabolic diseases, for example, diabetes, which is a disease that contributes to various infections, not just fungal.
The fungus is more common in obese people with anemia (anemia), disorders of the circulatory system that cause ischemia of the nail plate, and in patients with gastrointestinal disorders.
Nail fungus often affects patients who are treated with chemotherapy for malignant tumors who take antibiotics (especially if they are not accompanied by probiotics), as well as patients who, for various reasons, take steroid drugs known for their immunosuppressive effects, that is, they alter the functioning of the immune system.
There are four main types of nail fungus, no matter which part of the nail is affected. The most common type of fungus affects the far (distal) part of the nail, including the supraungual plate, that is, the skin located in front, under the nail plate.
Symptoms of nail fungus

Interestingly, nail fungus can initially be asymptomatic; in these cases, there is only an increase in brittleness and a slight discoloration of the nail plate. Only after a while, characteristic and pronounced changes in the appearance of the nail begin to appear.
Symptoms of nail fungus are, first of all, changes in the nails, especially in the initial stage of the development of the disease. The first changes usually appear on the free edge (front) of the nail plate or on the sides.
With the increased development of nail fungus, additional problems can arise with physical activity (for example, exercise) and even walking and standing. Then patients complain of paresthesia (numbness), pain, discomfort, loss of physical fitness. Characteristic changes within the nails during the course of the fungus include:
- color changes: nails turn white, yellow, brown, greenish,
- peeling and flaking of the nail plate, markedly increased brittleness,
- rippling of the nail plates,
- thickening of the nail plate, which is a symptom of excessive keratinization,
- unpleasant foot odor.
Fungi can present with various symptoms. Two different patients infected with the same type of fungus may experience different changes to their nails.
Toenail fungus can have a somewhat distinctive character. It can be called by the so-called. mold fungi. This form of fungus is often found in the elderly and is associated with poor blood supply to the nail (trophic disorders). The nail plates of the thumbs become thickened, deformed, acquire a greenish-yellow tint, and a significant thickening of the epidermis is observed under the plates. As a general rule, nail fungus lasts for many years without treatment. Unfortunately, even with proper and long-term treatment, this disease can recur.
The above symptoms are usually determined by the fungus. In addition to the characteristic appearance of the nails, the detection of a fungus on the skin of the feet and hands, which often accompanies a nail fungus infection, can help in the diagnosis of nail fungus. However, the diagnosis is not always obvious.
In some cases, additional laboratory tests are necessary. The doctor takes a sample and examines it under a microscope. Another auxiliary analysis in the diagnosis of nail fungus is the culture of the extracted fungi. Thanks to this, it is possible to determine its type and check the sensitivity to specific drugs.
If the doctor suspects a nail fungus in a certain patient, they should also consider other conditions that may have a similar picture, namely:
- Nail psoriasis: it may seem similar, however, the characteristic difference of this disease is that it often affects all the nails, symmetrically; In addition, psoriasis is often accompanied by typical skin changes;
- Candidiasis (or candidiasis) of the nails is another type of nail fungus, unlike the classic one, associated with infection by dermatophytes; it is characterized by the appearance of purulent discharge under the ridges of the nails, as well as pain;
- trophic changes caused by a violation of the blood supply to the nail plate; they generally begin proximal to the plate (ie, at its base);
- Lichen planus is a disease in which the appearance of papules (changes) on the skin and mucous membranes is characteristic, the simultaneous presence of which, as a rule, simply makes it possible to distinguish lichen from a fungus; the lichen nail plate has a characteristic longitudinal ripple.
When pressed, purulent contents appear. If the candida changes do not go away for a long time, the nail plates turn gray-yellow-brown, lose their shine, thicken and exfoliate.
Candidiasis of the nail plates and rollers must be distinguished from panaritium, that is, a bacterial infection, which differs, first, in that it is limited to a single finger and progresses more acutely, with greater pain. Also, yeast infection can be confused with "common" nail fungus and nail psoriasis.
To make a definitive diagnosis of candidiasis it is necessary to carry out a culture (culture of the Candida fungus). It is impossible to recognize mushrooms of this family in direct preparation, that is. examining the secretions extracted from a sore spot, without culture.
As a conclusion to the discussion of the symptoms of nail fungus, it is worth remembering the psychological problems that patients suffering from this disease may encounter. These include decreased self-esteem and worsening social contact. These problems can especially affect those who have a fungus affected by the nails.
Methods to treat nail fungus.

Treatment for nail fungus is essential. Lack of treatment for nail fungus leads to a chronic and progressive course of the disease. There can be no spontaneous recovery. Therefore, always in case of appearance of suspicious changes in the area of the nails of the palms or feet, it is necessary to go to an appointment with a dermatologist.
Even if it turns out that the cause of the disorder is not a fungal infection, only a dermatologist will be able to determine what disease the patient has.
Unfortunately, the treatment of the disease under discussion is difficult and not always effective. This is because the frustrated patient simply stops using the prescribed medication. For the course of treatment to be effective, its duration must be several months, even after the symptoms disappear.
In the initial stages of the fungus, when the changes in the nails are still insignificant, a fungicidal ointment will suffice. When the fungus starts, as a rule, oral agents are used. Relapses of the fungus are quite frequent, therefore, after recovery, you should follow the recommendations of a dermatologist and take care of foot hygiene. Many patients refuse treatment immediately after the disappearance of symptoms, and this is incorrect as it can lead to relapse and the need to start treatment again.
Home treatment for nail fungus is often ineffective.
Nail changes should be examined by a dermatologist. What you can do yourself to promote therapy is to maintain foot hygiene, wash and dry your feet well, not cut your nails too short, and not use other people's manicure kits, towels, socks, and shoes.
In general, the treatment of nail fungus depends on the type of infection, the clinical type of the disease, the number of infected nails, and the degree of damage to the plates. In some cases, systemic treatment through oral agents is necessary. Sometimes local treatment is enough, that is, ointments, creams. Without a doubt, the combination of systemic and local treatment improves the success rates of nail fungus therapy. Unfortunately, even with the use of the latest medications, the percentage of nail fungus relapse remains high. In the future, photodynamic and laser therapy may find application in the treatment of this disease.
Effective drugs for the treatment of nail fungus.
Local remedies without oral medications should be used only in cases where the lesion occupies less than half of the distal (far) part of the nail plate, and also when the patient does not tolerate systemic treatment well. These are rare cases; as a general rule, local treatment, unfortunately, is not enough.
As a general rule, local remedies used as the sole therapy for nail fungus cannot completely cure them as they do not penetrate deep enough into the plaque.
True, it was believed that the solutions penetrate all layers of the nail, but they are still ineffective if used in monotherapy (as the only medicine). However, these drugs can be used as "adjunctive" therapy, as an adjunct to an oral agent, or as prophylaxis for relapse in patients who have previously treated nail fungus with systemic (oral) agents.
Medicines for the treatment of nail fungus.
Oral treatment for nail fungus cases is almost always necessary. The latest generation of oral antifungal medications have recently replaced previous generations in the treatment of nail fungus. The effectiveness of the new agents lies in their ability to penetrate deep into the nail plate a few days after the start of treatment.
Through its use, it is possible to allow a reduction in the duration of therapy, while achieving a higher percentage of recovery and fewer side effects.
In the case of therapy through these means, patients must arm themselves with patience and calmly wait for a healthy nail to grow back after the treatment is finished. This may take longer.
Remove nail fungus
Removal of fungal affected nails is also considered a solution. For nail fungus, surgical treatment can be used. Here we are talking about the mechanical or chemical removal of the infected nail plate. Chemical plaque removal is possible using a 40-50% urea solution. This is a painless and effective method in cases where the nail is very thick.
Nail plate removal should be considered as an adjunct treatment for patients on oral therapy. The combination of oral, local treatment (lubrication), as well as surgery, gives a higher percentage of cure and at the same time is the most effective and cheapest option (minimal relapses, short-term treatment).
During the treatment of nail fungus, it is not necessary to restrict activities in a broad sense, but it is recommended to avoid places where contamination can occur, such as public swimming pools.